Palestine

A poster from Cuba depicts Jesus the revolutionary.
By Phil Shannon

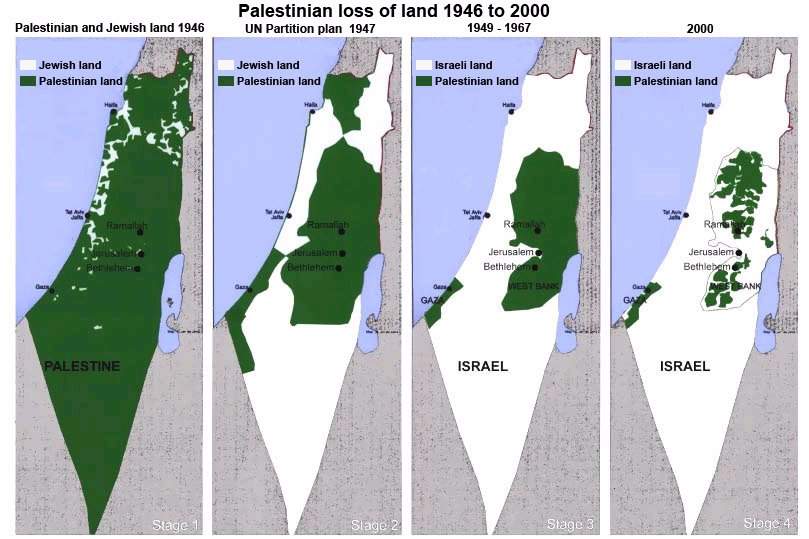
In 1948, more than 800,000 Palestinian men, women and children were forced to flee their homes.
COSATU leader on South African and Israeli apartheid

Address by Zwelinzima Vavi, general secretary of
BDS campaign declares: 'Occupy Wall Street not Palestine!'

[For more on the BDS campaign click HERE. For more on Occupy Wall Street, click HERE.]
If a people one day wills to live fate must answer its call
And the night must fade and the chain must break– Abou-Al-kacem El-Chebbi (Tunisia)
We are part of the world’s 99% yearning for freedom, justice and equal rights!
Palestine: Ilan Pappe -- At the UN, the funeral of the two-state solution
By Ilan Pappe
September 12, 2011 -- Electronic Intifada -- We are all going to be invited to the funeral of the two-state solution if and when the UN General Assembly announces the acceptance of Palestine as a member state.
The support of the vast majority of the organisation’s members would complete a cycle that began in 1967 and which granted the ill-advised two-state solution the backing of every powerful and less powerful actor on the international and regional stages.
Even inside Israel, the support engulfed eventually the right as well as the left and centre of Zionist politics. And yet despite the previous and future support, everybody inside and outside Palestine seems to concede that the occupation will continue and that even in the best of all scenarios, there will be a greater and racist Israel next to a fragmented and useless bantustan.
Does Palestinian Authority’s UN 'statehood' bid endanger Palestinian rights?

Palestinian Authority envoy to the United Nations Riyad Mansour.
By Ali Abunimah
August 8, 2011 -- Electronic Intifada -- The Palestinian Boycott National Committee (BNC), the steering group of the international boycott, divestment and sanctions (BDS) campaign, has issued further guidance in the run up to the Palestinian Authority’s effort to gain UN membership for a “State of Palestine” in September.
The BNC statement implicitly warns that recognition of any “state” that did not include full recognition of all Palestinian rights and the right of all Palestinians everywhere to be represented, could violate or negate those rights.
The statement further warns that governments around the world cannot use symbolic recognition of a Palestinian “state” to evade their responsibilities.
