economics

Would Marx approve this year’s Nobel?
Dmitry Pozhidaev — Innovation won the Economic Nobel this year. But would Karl Marx approve? Partly.

Long wave theory, globalisation’s end, and the coming crises: An interview with William Jefferies
William Jefferies explores the usefulness of long wave theory for understanding the current moment, how globalisation reshaped the world economy, and the coming period of crisis.
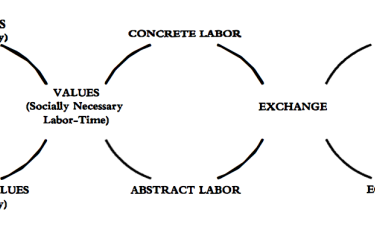
Marx’s critique of political economy: The logic of the commodity
Jason Devine provides an overview of the intellectual roots of Marx’s approach and explains the dialectical logic of his analysis of the commodity.

From billions to trillions to traps: Rethinking development finance from the periphery
Dmitry Pozhidaev — Only by addressing structural imbalances and grounding finance in transformative, locally rooted practices, can development finance truly become developmental.

The declining rate of profit: Avoiding the key issue
William Jefferies — James Doughney’s latest contribution to the discussion on Marx’s tendency of the rate of profit to fall avoids the key point: the relationship between the proportional rise in the mass of physical capital and productivity rate rises.

The declining rate of profit: Déjà vu all over again
James Doughney responds to William Jefferies critique of his article “Marx was wrong about the declining rate of profit. Isn’t it time we put this false idea to rest?”.
Was Marx wrong about the declining rate of profit?
William Jefferies — James Doughney’s attempted refutation of Karl Marx’s law of the tendency of the rate of profit to fall is thoughtful and thorough, but ultimately wrong.




